Melanoma
Lymph Node Mapping
A procedure known as sentinel lymph node mapping is recommended when there is an increased risk the primary melanoma may have spread to nearby lymph nodes. This procedure tracks the exact path of lymph (the bodily fluid that carries white blood cells) as it drains from the skin surrounding the melanoma to the nearest lymph node. The draining lymph node closest to the melanoma is called the sentinel lymph node (SLN). Accurately identifying which lymph node is the SLN is important because the decision to remove lymph nodes often depends on whether melanoma has spread to an SLN. This helps determine the stage as well as the need for genomic testing, which in turn, guides treatment.
Lymph node mapping (lymphoscintigraphy) is a special type of imaging technique done in a hospital’s nuclear medicine department the day before or the day of surgery to remove the melanoma. A radioactive tracer is injected into the skin around the site of the melanoma, and an imaging device that detects radioactivity makes a series of images that show the path of the radioactive material as it travels to the nearest group of lymph nodes.
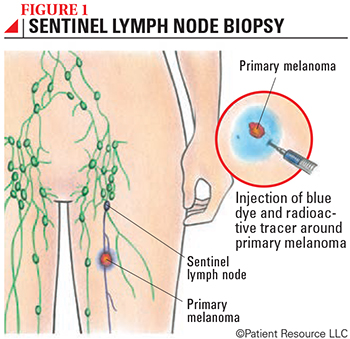
During an SLN biopsy, the surgeon will inject a blue dye into the skin around the site of the melanoma to visually identify the SLN (see Figure 1). The surgeon will then make a small incision in the area of the lymph nodes and remove the SLN, which can be identified by the blue dye and the presence of the radioactive tracer as detected by a handheld device. The node(s) are then carefully examined by a pathologist for the presence of melanoma cells. Because the SLN is the first place to which lymph drains from the site of the melanoma, it’s highly unlikely the melanoma will have spread to any other lymph nodes if no cancer cells are found in the SLN.
This procedure involves a team of experienced physicians: a radiologist specializing in nuclear medicine imaging who reviews the images; a surgeon who injects the blue dye and performs the biopsy; and a pathologist who evaluates tissue from the SLN to see if melanoma cells are present.